Bachelor of Business Administration

- Overview
- ISLOs
- Eligibility
- Modules
- Fees
- Apply Now!
Blended Method:
The program is available in person or online through our blended study method. Every class session is live-streamed online and recorded onto our online platform, allowing our students to have all the tools they need to be successful in their program
The Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) is designed to give a broad knowledge of the functional areas of a company and their interconnection while also allowing specialization in a specific field. BBA programs expose students to various subjects and allow students to specialize in particular academic areas. The degree also develops the student’s practical managerial communication skills. The program incorporates training and practical experience through case studies, presentations, internships, industrial visits, and interaction with experts.
The Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) is a full-time, 180 ECTS program divided into three years; Sophomore, Junior, and Senior. Students who did not complete their Freshman year in their Secondary studies may be required to complete a Freshman level course before they continue to this program. The Swiss School of Management offers the Freshman year through our collaboration with study.com. Classes are lectured by qualified faculty with an International Curriculum. Students also participate in internships, company visits, excursions, forums, symposia, guest speaker presentations/webinars, e-conferences, and much more.
The program culminates with the submission and defense of a thesis on a business-related subject of the student’s choosing. Students who complete the program are awarded the Bachelor of Business Administration degree from the Swiss School of Management.
The Swiss School of Management utilizes an innovative approach to team-based online learning as the Swiss School of Management strongly believes that this approach reflects today’s progressive workplace. The Swiss School of Management’s Bachelor of Business Administration program will open the door to international career opportunities by preparing students for global business.
Intended Student Learning Outcomes (ISLO’s):
Students seeking admission to the BBA program must have completed their secondary education equivalent to:
- Swiss Matura, German Abitur, French Baccalaureate, English ‘A’ levels or Italian Diploma di Scuola Secondaria Superiore.
- International Baccalaureate, a US High School Diploma, International general certificate of secondary education (IGCSE) at ordinary level (O Level) and general certificate of education at advanced level (GCE A level) with 7 different subjects (5 at ordinary level and 3 at advanced level)
- All Arab official secondary certificates (As certified by local governments)
All other applicants with 12 years of schooling up to high school who do not satisfy any of the above conditions stated in items 1, 2 and 3 (such as the US) should enroll via study.com in our collaborated freshmen program to accomplish 30 credits of general education courses before joining the sophomore year.
Students who must complete a foundational year of study must enroll in general education modules through study.com to be eligible for enrollment into the 3-year BBAprogram.
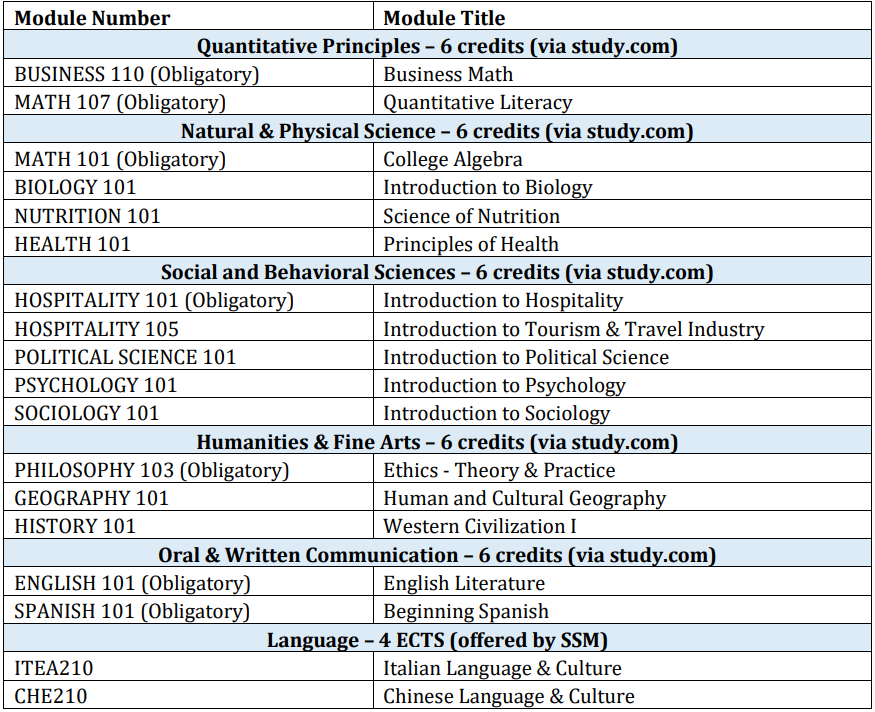
Students who must complete a foundation year will be informed by their Site Director before enrollment. For more information on students require a foundation year, please consult the Registrar by emailing logan.pacey@ssm.swiss.
Documents presented in any language except English, Italian, German, Spanish, and French require translation from a legal sworn translator.
Applicants for the Bachelor of Business Administration program are exempted from an English Exam provided they completed their secondary schooling at a recognized school where the medium of teaching is English.
In case this condition is unmet, then, the applicant needs to sit for one of the listed English exams:
– Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL PBT) – minimum score: 57
– Internet Based Test (iBT) – minimum score: 61
– International English Language Test (IELTS) – minimum score: 6.0
– Pearson Test of English Academic Score Report – minimum score: 44
– Duolingo English Test – minimum score: 95
– 4-skill Michigan English Test (MET) – minimum score: 53
– Michigan Examination for the Certificate of Competency in English (ECCE) – minimum score: 650/LP
– Michigan Examination for the Certificate of Proficiency in English (ECPE) – minimum score: 650/LP
SSM allows candidates who do not hold recognized secondary school certificates as per the entry criteria to enrol at the BBA program Level and take courses toward a degree from SSM.
Such applicants should have gained at least 10 years of leadership experience and passed any of the designated internationally approved English Exams stated within the entry criteria section of the BBA program.
Applicants aiming to join the BBA program and who have already started a bachelor’s level program in an authorized institution other than SSM are subject to the below transfer policy:
– An official transcript of record showing courses and grades earned must be scanned.
– The admissions department validates the authenticity/legality of the transcript and its issuing institution.
– Documents presented in any language except English, Italian, German, Spanish, and French require translation from a legal sworn translator.
– Once authenticity is proven, a copy the transcript is sent to the transfer committee comprised of the Academic Dean and Head of Admissions.
– The Academic Dean matches and maps the transcript courses with a passing grade against SSM’s list of courses for transfer equivalence decisions. Certain courses, even though passed, might not be transferred in case they substantially differ from SSM’s bachelor’s courses.
– The committee then approves transfer of credits of courses that are only passed and strictly denies transferring credits of failed courses based on the Academic Dean’s transfer equivalence decision.
– The number of credits to be transferred are modified so that they fit a common practice or norm used for conversion into the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS).
– SSM grants up to 40% credits to transferring students of the BBA program requirements at SSM; thus, students need to accomplish at least 60% of their course requirements at SSM so that they earn SSM’s Bachelor’s degree.
Overview:
The first year of the Bachelor of Business Administration degree explores in-depth and complex contexts of how businesses’ goals ensure they gain and maintain a competitive advantage. This is equivalent to the Sophomore year of the three-year Bachelor Administration Program level. The Program awards 60 ECTS or 30 US Credits.
The three-year course begins with the fundamentals of business administration, which positions students for advanced options later in the program. The Swiss School of Management’s undergraduate curriculum is designed to give students the maximum degree of choice and flexibility while also providing insights into all management’s major fields and functions. Students will take business courses from many different disciplines and will have the opportunity to concentrate on one or several significant areas in the third year of study.
The first year allows students to gain experience in these disciplines before they choose their
concentrations. Within this period, different modules provide the program with an educational
environment where students can:
• Build an up-to-date knowledge base and develop skills that will prepare them in the
field of Business Administration and the related markets at all operational levels.
• Acquire professional skills and competencies through a balance between practical and
lecture-based learning environments.
• A guided learning environment, based on a sound acquisition of technical skills and
training to guide participants to acquire a work ethic that is typical of the Swiss culture.
Furthermore, the practical learning-based approach offers opportunities to acquire lifelong skills
such as teamwork, leadership, interpersonal communication, and time management.
MODULE NUMBER |
MODULE TITLE |
MODULE TYPE | TOTAL COURSE CREDIT/ CLOCK HOURS |
| BUS 200 | INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| BEN 201 | BUSINESS ENGLISH | Elective | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| FIN 210 | INTRODUCTION TO FINANCE | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| MKT 210 | INTRODUCTION TO MARKETING | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| STA 210 | MANAGERIAL STATISTICS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| COM 210 | COMMUNICATION SKILLS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MIS 210 | MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| ACC 210 | MANAGING ACCOUNTING COSTING AND BUDGETING | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| MGT 210 | MANAGEMENT | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| MAT 210 | MATHEMATICAL TOOLS FOR BUSINESS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| ECO 210 | ECONOMICS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| COR 210 | COMMERCIAL CORRESPONDECE | Core/Required | 1 US Credits / 2 ECTS |
| TQM 210 | TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| SMG 220 | SALES MANAGEMENT | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| ITEA 210 | FOREIGN LANGUAGE | Elective | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| CHE 210 | FOREIGN LANGUAGE | Elective | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| LAW 220 | BUSINESS LAW | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| LEA 220 | LEADERSHIP MOTIVATION & GROUP DYNAMICS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits/ 4 ECTS |
| INT 220 | INTERNSHIP | Capstone | 1 US Credit/ 2 ECTS |
Year 1 Module Descriptions:
This module is designed as a survey course that will expose you to business terminology, concepts, and current business issues. The intent is to develop a viable business vocabulary, foster critical and analytical thinking, and refine your business decisionmaking skills.
This module is designed for non-native English speakers. It aims to improve their oral, written, and listening comprehension language skills while making them more effective communicators in a business environment. In addition, the individual and group activities focus on continuously increasing their use of appropriate vocabulary and grammatical structures while learning how to negotiate and make effective presentations.
This module aims to help students acquire skills in the main principles of Finance and its application to the Business world. In particular, students will learn the impact of Finance in Business, the basic Capital Investment Decisions, and the Management of Working Capital. Finally, students will learn some techniques for Financing a Business.
This module introduces students to the concepts and skills needed to create and critique effective marketing. Marketers in all organizations require an understanding of the many facets of marketing, beyond simply advertising or communications.
This module aims to help students acquire skills in the elaboration, representation, and interpretation of business data with the support of statistical and mathematical tools. In particular, students will learn how to process and present in MS Excel some essential data. Finally, students will learn how to apply descriptive statistical measures to businesses.
The module will be divided into 16 Chapters, Assignments, and Final Written Exam. It will take students through oral and written business communication skills, critical thinking and analytical reasoning, ethical decision-making, teamwork, and professionalism.
Student participation in class, including homework, Assignment, and Final exam, represent the tools for evaluating the students (see Table 1). These practices will comprise critical thinking, theory, case study, and actuality.
Students will be motivated to perform interactive activities and participate actively by brainstorming, presenting, attending, and asking questions. Enhancing presentation and writing skills will be an integrated task.
Computers are everywhere. Software is eating the world. The introduction of the iPhone started the Digital Era, a period of explosive digital diffusion. During the Covid19 pandemic, digital has been helping us not only to survive, but to maintain and even foster personal relations as well as to work and manage businesses remotely.
The objective of this module is to help students to acquire skills in the main principles of Accounting and its application to the Business world. In particular students will learn the principal Financial Statements, the main Accounting Principles and Concepts, the Financial Reporting and Budgeting processes. Finally, students will learn some fundamentals of Cost Accounting and Performances Measurement.
Management is the process of achieving organizational goals by engaging in the four functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Management entails reaching important goals and involves knowing how to perform the major functions of management. The module aims at introducing the major functions of management and providing an overview on activities within organizations.
This module aims to prepare the students to meet the demands of today’s business world with the proven, practical dual approach to using MS Excel. In particular, students will learn the traditional methods of calculating. Finally, the students will learn the essential functions of MS Excel in applying the Math concepts.
The module will be divided into 16 Chapters, an Assignment, and a Final Written Exam. It will take students through oral and written business communication skills, critical thinking and analytical reasoning, ethical decision-making, teamwork, and professionalism. Student participation in class, including homework, Assignment, and Final, Exam represents the tools for evaluating the students (see Table 1). These practices will comprise critical thinking, theory, case study, and actuality. Students will be motivated to perform interactive activities and participate actively by brainstorming, presenting, attending, and asking questions. Enhancing presentation and writing skills will be an integrated task.
This module will introduce you to the economic principles and policies affecting the economy while also introducing you to ethical principles, how they relate to economic principles, and how they may affect policies and the economy. Concerning economic principles, we will examine both microeconomics (the study of individual decision-making by consumers and businesses) and macroeconomics (the study of social-level problems that most often are reported in the evening news, e.g., economic growth, inflation, unemployment, government spending, and taxes, money and interest rates and international exchange and trade). Concerning ethical principles, we will briefly examine ethical principles in general but focus on the applications of ethical principles in economic contexts. This course aims to introduce you to the terms and concepts of economics and ethics that will allow you to understand and critically analyze the economy’s condition, the various economic policies proposed to help the economy, and the role ethics play in shaping financial performance and policies.
The module will take students through focus, statistical methods, controlling, and measuring quality to obtain a holistic view of total quality management. The scope is to understand quality assessment and how to monitor quality clearly. A final examination will complement presentations in creating the final grade. Students will be motivated to participate actively by presenting, attending, and asking questions.
The module will be divided into ten Chapters, an Assignment and a Final Written Exam. It will take students through personal selling, objectives and strategies of personal selling, including communication skills, building trust, planning, customer service, adding value etc. The scope is to obtain a clear and direct understanding of sales process and how to optimize sales by meeting the client’s needs.
In communicating with Italians, language learners have to meet linguistic challenges such as understanding the information presented to them in terminology meant for native speakers, making sense of it, speak or acting accordingly. We aim at promoting the ability of learners to manage under such demanding circumstances by simulating this process in class, with the support of the teacher and the aid of the group (theorists call this an action-oriented approach). At the same time and along the way, we point out, try to make sense of, explain and clarify, practice all the major structures of the language in their cultural context in order to ensure accuracy of communication.
This is an entry-level Chinese class for beginners who are interested in Chinese culture and language. It is useful to know about the language when coming to China for travel or business. Participants will not only be exposed to authentic language contexts, but also to situations where their abilities to use the Chinese language to do creative dialogues. All the learning materials chosen reflect the value system, traditions, daily life, social development, and business-oriented conversations of the current Chinese society.
Business Law, Commercial Law, and European Law are legal fields that have gained in
importance in recent decades and have increased due to the globalization of economies and the related development of international commerce. We can affirm that Business laws establish the rules that all businesses should follow. This module will introduce students to business law’s basic concepts and problems of Business Law and the International legal system. The module will cover the main topics in this field. Such as the basic principles and sources of EU Law, International Law, and the legal order; the Four Freedoms; the settlement of disputes. Competition Law, Unlawful agreements and concerted practices, Abuse of a dominant position and price policy, Torts, contracts, and Negotiable instruments, the Lifecycle of a Business agreement, and the new EU GDPR principles.
This module aims to unveil the rationales for bringing change in organizational settings and examines the role of strategic leadership in managing organizations. It delves into the details of the nature and processes of an organizational change with a focus on technological, administrative, and process innovation. This module, case studies, class exercises, and projects will provide students with a way forward to critically evaluate the process of change management and strategic leadership in organizations.
You must bring proof of at least two months of Internship experience in a local (or virtual-remote) business. In alternative to an internship, would a Study-Abroad experience also be accepted. For the latter option, you must produce a certificate of attendance or academic transcripts from the host institution.
Overview:
In the second year of the three-year program, students expand on the fundamentals they learned during the first year of study. Students will take a critical and practical approach to the core concepts of business administration and management. This is when students begin to move past foundational knowledge and dive deep into the concepts covered in the first year. At the end of the academic year, second-year students will have the opportunity to apply their knowledge in real-life situations through the required internships, which facilitates students to have a skillset beyond just theory but sought-after real-life practical skills in the job market today. This is equivalent to the Junior year of the three-year Bachelor Administration Program level. The Program awards 60 ECTS or 30 US Credits.
This program provides more advanced knowledge, understanding, and skills that will enable students to:
– Develop an understanding of the professional world through case studies and field research;
– Build an up-to-date knowledge base of management skills applicable to Business Administration within a context of understanding the broader industrial and economic interests.
MODULE NUMBER |
MODULE TITLE |
MODULE TYPE | TOTAL COURSE CREDIT/ CLOCK HOURS |
| ACC 310 | ADVANCED ACCOUNTING | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| FIN 300 | VENTURE CAPITAL AND PRIVATE EQUITY | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MIS 300 | MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS: DECISION SCIENCE I | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| HRM 300 | HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MKT 300 | PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MBK 300 | MONEY AND BANKING BUSINESS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MKT 310 | CONSUMER BEHAVIOR | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| ECO 300 | INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MIS301 | MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS: DECISION SCIENCE II | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| FIN 310 | PRINCIPLES OF FINANCE | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MGT 310 | INTERCULTURAL MANAGEMENT | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| LEA 310 | LEADERSHIP AND CHANGE MANAGEMENT | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| FOL 300 | FOREIGN LANGUAGE 3 | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| INT 310 | INTERNSHIP | Capstone | 4 US Credits 8 ECTS |
Year 2 Module Descriptions:
This module aims to help students further develop their skills in some important Accounting topics. In particular, students will learn the principles of Financial Reporting of Accounting information, how to allocate overheads, and how to use Accounting for Control purposes. Finally, students will learn some techniques for measuring business performance.
In this module students learn how investment banks, VC, and private equity firms operate. Venture capital, private equity, debt and equity financing, financial derivatives, capital structure, investment research, and investing, among other financial topics, are studied and discussed. We cover the functioning of financial markets, analysis of risk and return, analytic tools, valuation of financial assets: stocks, bonds, options; investigative and research techniques, such as reading 10K’s, and other public filings for opportunity; valuation methodologies; and qualitative investigative techniques such as talking to company managements.
Good management implies good business decisions. Good business decisions are paramount to excel in running business processes. In any situation exists an optimal path to follow to achieve the strategic goals, and the disciplines of Artificial Intelligence and Operations Research can help find this optimal path among an infinite number of options. When applied to business decisions, those disciplines are typically known as Decision Science, and the tools used in this field are called Business analytics (BA). Business analytics (BA) is the practice of iterative, methodical exploration of an organization’s data via the processing and storage power of modern Information Systems. BA is used by companies committed to data-driven, bottom-up decision-making. BA enables organizations to gain insights that inform business decisions and can be used to automate and optimize business processes. Data-driven companies treat their data as a corporate asset and leverage it for a competitive advantage. Successful business analytics depends on data quality, skilled analysts understanding the technologies and the business, and an organizational commitment to data-driven decision-making.
The module will cover both an overview of the mathematical basics that are behind BA and their possible application limitations, as well as the BA’s significant applications in different Vertical Markets, with a particular focus on Retail. A critical implication of the BA application is Change Management, and a part of the course will be dedicated to this topic.
This module explores the management of human resources from an overview perspective. Topics covered are payroll, compensation and benefits, staffing, training and development, performance appraisals, organizational management, policy, and maintaining effective employee relationships. Students will be exposed to the dynamics of how the human resource department and the company strategically work together to balance employee morale and return on investment. Thought-provoking questions will initiate a well-rounded learning experience of HRM and its business operations.
Students acquire the knowledge and skills required to develop, implement, and control successful marketing strategies. Topics include the art of case analysis; consumer behavior; marketing research and competitive analysis; marketing segmentation and position; market entry and pricing; retail selling, private labels, and channels of distribution; marketing communications; Internet marketing; corporate social responsibility and nonprofit marketing; sales management; and international marketing.
This module explores the functions, operations and efficacy of the global financial system, highlighting the significant changes that have occurred in recent decades. Globalisation and innovation have transformed the challenges facing both private institutions and public regulators. Moreover, the Great Financial Crisis forced a wide-ranging debate on the value of financial intermediation in the modern world and the need to overhaul the global system of public oversight. We translate the jargon of money and banking into plain language; explain the basic principles behind key financial instruments such as repos, futures, swaps, CLOs and other alphabet-soup derivatives; shine a light on “shadow” banking; outline the thinking behind the current financial reform programme (Basel III); reveal how central banks operate monetary policy and why they sometimes pursue different approaches in tackling 21st century challenges.
Analyzes consumer motivation, buying behavior, market adjustment, product innovation, and adaptation; consumer market measurement, including a survey of economic and behavioral science theories of consumer market behavior, producer and intermediary reactions. Consumer decision-making is evaluated as to psychological drives, and sociological concepts used by producers, channel intermediaries, and consumers; it considers methods and techniques for measuring consumer behavior and analyzing consumer markets.
This module aims to help the students acquire skills in macroeconomics theory linked to business management across all fields. In particular, the students will learn the practical use of macroeconomics and how it affects the decision-making process—the main macroeconomic variables affecting business decisions and the potential strategies to adopt. Finally, the students will learn basic methodologies to present their analysis and draw their main conclusions.
Good management implies good business decisions. Good business decisions are paramount to excel in running business processes. In any situation exists an optimal path to follow to achieve the strategic goals, and the disciplines of Artificial Intelligence and Operations Research can help find this optimal path among infinite number of options. When applied to business decisions, those disciplines are typically known as Decision Science, and the tools used in this field are called Business analytics (BA). Business analytics (BA) is the practice of iterative, methodical exploration of an organization’s data via the processing and storage power of modern Information Systems. BA is used by companies committed to data-driven, bottom-up decision-making.
BA enables organizations to gain insights that inform business decisions and can be used to automate and optimize business processes. Data-driven companies treat their data as a corporate asset and leverage it for a competitive advantage. Successful business analytics
depends on data quality, skilled analysts understanding the technologies and the business, and an organizational commitment to data-driven decision-making. The course will cover both an overview of the mathematical basics that are behind BA and their possible application limitations, as well as the BA’s significant applications in different Vertical Markets, with a particular focus on Retail. A critical implication of the BA application is Change Management, and a part of the course will be dedicated to this topic.
The module aims to develop in students an understanding of the basic principles of finance. It builds on the introduction to finance provided in Foundations of Business. The module has a quantitative slant, and is designed to give a theoretical introduction to financial markets and company finance policies. It is a prerequisite for finance Honours courses. The course looks at the way assets are valued in financial markets. It considers interest rates and the pricing of fixed-income bonds; stock market prices and returns; stock market risk and the influence of risk on the pricing of shares; and the characteristics and pricing of financial futures and options. The module also covers some aspects of company finance theory. These include business investment decisions, sources of finance, the cost of capital, the financial structure decision and the dividend decision.
The module will also support the development of students’ skills in the areas of cultural sensitivity and ability to create more sophisticated conceptions of cross-cultural encounters. It will move the students from the traditional dualistic ‘black or white’ way of thinking further towards a more relativist one ‘with all shades of grey in between’. The module focuses on the impact of cultural background on individuals, organizations and management; on the dimensions which discriminate national cultures, and on cross-cultural interactions. The objective of the module is to help students to construct their own coherent, individual perspective of the substance and increase their cultural awareness.
This module is aimed at unveiling the rationales of bringing change in the organizational settings and examines the role of strategic leadership in the management of organizations. It delves into the details of nature and processes of the organizational change with a focus on technological, administrative, and process innovation. This module helps students to explore contemporary techniques and procedures used to understand, initiate, plan, implement and communicate change. Lectures, case studies, class exercises and projects will provide students a way forward to critically evaluate the process of change management and strategic leadership in organizations
In the second your of your Bachelor’s Studies, you will learn another new language and culture.
Here are another 5 good reasons to learn a foreign language: 1. Foreign language study will completely improve your traveling experience. 2. As immigration increases, we must prepare for American society’s changes. 3. One is at a distinct advantage in the global market if one is as bilingual as possible. 4. Foreign languages open the door to art, music, dance, fashion, cuisine, film, philosophy, and science… 5. Foreign language study is simply part of an elementary liberal education: to “educate” is to lead out, out of confinement, narrowness, and darkness. The School will communicate before starting the new academic year which foreign language will be chosen for this course.
You must bring proof of at least two months of Internship experience in a local (or virtual-remote) business. In alternative to an internship, would a Study Abroad experience also be accepted. For the latter option, you must produce a certificate of attendance or academic transcripts from the host institution.
Overview:
The objective of the program’s final year leading to the Bachelor of Business Administration Degree is to provide the student with a solid and well-rounded education in business and business administration. A primary core curriculum offers an accounting, management, marketing, and economics foundation. This core is augmented by specialized courses to meet individual goals and career objectives. Special emphasis is given to personality development to become a competent manager or entrepreneur. It concludes with submitting a thesis paper presenting the research results and analysis of a business problem. The basic philosophy of this program is to train the student to become a mature, conscientious, and responsible individual who is sincere in their desire for education. The final year of the program advances participants in Business Administration from a basic understanding to a specialized foundation by providing opportunities for students to:
– Construct and elaborate creative thinking skills such as reflective, critical, and realistic thinking.
– Develop a strong sense of entrepreneurship, business ownership, and financial acumen that prepares students to perform in a competitive economic environment.
– Experience a proper personal development path intended ultimately to help situate, plan, and set realistic career goals for achieving a fulfilling personal and professional pathway.
– Students have the prerogative of choosing their specialization (major) in their third year of study.
| COURSE NUMBER | COURSE TITLE | COURSE TYPE | TOTAL COURSE CREDIT/ CLOCK HOURS |
| FIN 410 | INTERNATIONAL FINANCE | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MKT 430 | STRATEGIC MARKETING | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| ICT 410 | INFORMATION SYSTEMS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| FOL 400 | FOREIGN LANGUAGE | Elective | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| FIN 420 | FINANCIAL PLANNING & BUDGETING | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| MGT 410 | ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| LEA 450 | STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP AND CHANGE | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| GLB 410 | BUSINESS IN A WORLD ECONOMY | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| ICT 410 | INFORMATION SYSTEMS | Core/Required | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS |
| INT 410 | INTERNSHIP | Core/Required | 3 US Credits 6 ECTS |
| GRD 499 | THESIS | Capstone | 3 US Credits 6 ECTS |
| International Week |
Year 3 Course Descriptions:
This course mainly focuses on international financial management, viewed primarily from the perspective of managers doing business overseas, including managing foreign exchange exposure, foreign direct investment decisions, and multinational capital budgeting. Other topics covered include trends in international banking, the balance of payments, the determination of exchange rates, and the LDC debt crisis. Such issues as financing international trade and country risk analysis for investment decisions will also be covered.
The philosophy underlying this course is that marketing-oriented companies put customers first, are geared for long-term success, and that this orientation must be championed by top management and infused throughout the organization. In addition to this overall culture, strategic marketing requires knowledge, skills, and competencies in various techniques, such as strategic analysis and planning, implementation via several integrated and synergistic marketing functions and activities, and marketing control aided by multiple marketing metrics and digital developments. This course aims to provide students with a firm grasp of the strategic elements of establishing a long-term customer orientation and the operational techniques required of marketing managers to implement a strategic marketing orientation successfully.
Permanent innovation, disruptive technological, social, and economic changes are critical characteristics of the “New” Economy, drastically impacting on any part of our business and personal life. Information Technology (IT) is at the center of the Digital Transformation of companies for the optimization, redesign, or reinvention of their business in response or, better, in anticipation of the disruptive impact of emerging technologies and new business models. All managers are directly or indirectly concerned with IT. Either because they work in the IT department or are involved in defining, purchasing, deploying, and using IT infrastructures, software, and applications.
For the third year in a row, you will be facing a new challenge by getting to approach a new language among the following: German, Italian, Russian, Chinese, Hindi, or Spanish.
This course explores how current economic conditions impact household finances before showing you how to manage yours more effectively. You will find out whether you have bad financial habits and how to address them; discover a simple four-stage model for making sound financial decisions; examine the two components of household budgeting – income and expenditure – and how to manage them; and look at a key area of household spending – insurance.
This case and experience-based course focuses on behavioral aspects and the interactions between the firm and its employees. It strives to trace a path that is informed by various science-based disciplines (most notably social psychology) and is directly relevant to the practice of management in the firms of today and tomorrow.
This course aims to unveil the rationales for bringing change in organizational settings and examines the role of strategic leadership in managing organizations. It delves into the details of the nature and processes of organizational change, focusing on technological, administrative, and process innovation. This course helps students to explore contemporary techniques and procedures used to understand, initiate, plan, implement, and communicate change. Lectures, case studies, class exercises, and projects will provide students with a way to critically evaluate change management and strategic leadership in organizations.
This course offers an overview of various aspects of the global economy within the field of economic geography and its linkages to related issues of resources, development, international business, and trade. It investigates the phenomenon of globalization and seeks to provide an understanding of today’s increasingly interdependent world. Geographers are interested in examining the difference location makes to how economic activity is organized as globalization makes small differences among places increasingly important. This course recognizes that the economy cannot be treated separately from other social studies domains, so topics such as political, economic theories and models, historical context, consumption trends, the role of telecommunications, and others will be discussed.
You must bring proof of at least two months of internship experience in a(or virtual-remote) business. An alternative to an internship would be a Study-Abroad experience which will also be accepted. For the latter option, you must produce a certificate of attendance or academic transcripts from the host institution.
Professional and academic research are vital necessities for modern leaders to forge ahead. Research is the process of asking the right and relevant questions and of gathering and analysing the necessary data in a systematic and methodologically sound manner. An important aspect of sound professional and and academic research is to embed the research within the body of existing knowledge (applied research) and to add to it (generating new knowledge). This course will introduce the students to the basics of academic research, a pre-requisite before they start writing their thesis. The students will be trained to identify excellent research ideas, write and analyse data that leads to a relevant and timely contribution
GLOBAL MANAGEMENT (3 out of 4) | ||||
MGT 420 | NEGOTIATION SKILLS | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
MGT 430 | COMPETITIVE STRATEGY | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
MKT 450 | CASES IN MARKETING | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
FIN 450 | CASES IN FINANCE | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
INTERNATIONAL MARKETING MANAGEMENT (3 out of 4) | ||||
MKT 410 | CONSUMER BEHAVIOR | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
LMG 410 | LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
MKT 425 | NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
MKT 435 | SERVICES MARKETING | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
ENTREPRENEURSHIP (3 out of 4) | ||||
MGT 435 | FAMILY BUSINESS MANAGEMENT | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
MGT 440 | CASES IN ENTREPRENEURSHIP | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
MGT 445 | ADVANCED CASES IN ENTREPRENEURSHIP | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
FIN 460 | MERGERS AND ACQUISITIONS | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
FINANCE | ||||
FIN 420 | CONTEMPORARY CORPORATE FINANCE | Specialization | 3 US Credits 6 ECTS | |
MGT 415 | STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT | Specialization | 2 US Credits 4 ECTS | |
FIN 425 | COST CONTROLLING & FINANCIAL PLANNING | Specialization | 3 US Credits 6 ECTS | |
Specializations:
BBA in Global Management
Students will learn to navigate national cultures when negotiating deals, resolving disputes, and making team decisions. Rather than offering country-specific protocol and customs, Negotiating Globally provides a general framework to help negotiators anticipate and manage cultural differences, incorporating the lessons of the latest research with a new emphasis on executing a negotiation strategy and negotiating conflict in multicultural teams. We explain how to develop a negotiation planning document and show how to implement the plan, how the cultural environment affects negotiators’ interests, priorities, and strategies, how to distinguish good deals from poor ones and good negotiators from poor ones as well as how resolving disputes is different from making deals, as well as emphasizing on how negotiation strategy can be used in multicultural teams.
The module intends to demonstrate that decisions affecting the firm’s expansion are neither obvious nor entirely determined by the technological or economic forces generally associated with globalization. The module focuses on the concepts of Porter as well as SWOT analysis. Comparisons are drawn between the differences in the fundamental economic, financial, and political factors affecting the firm’s international expansion from purely domestic factors.
The module studies that the internationalization of the firm is a sequential decision-making process operating at the country, industry, corporate, business, and subsidiary levels of analysis. This module introduces students to the subject of strategy and helps them understand more thoroughly the overall impact of internal and external influences on the firm. The primary purpose of the module is to provide the student with broad insights into the practice of strategic management and its real significance in contemporary multi-national corporations
This module guides you through various Marketing case studies of real businesses using the Harvard Business School Case method.
This module guides you through various Finance case studies of real businesses using the Harvard Business School Case method.
BBA in International Marketing Management
This module introduces the theory of consumer behavior and relates it to the practice of marketing. It will present relevant material drawn from psychology, anthropology, and social and behavioral sciences within the framework of the consumer decision process and its main influencing factors.
You’ll learn from the ground up how a business is run from the ground up, getting principles you can later apply to your own business projects. Coursework focuses on ownership philosophies, business regulation, and structures that can be used to create well-managed businesses. Special topics include employment hierarchies and management structures.
Innovation and new product development are critical to the success of organizations and nations alike. Being first to market with innovative goods or services is essential in increasingly dynamic environments. The interplay between creative, market, and technical requirements is a highly complex process, whether the innovation is new to the world or an incremental development of existing products. Specific outcomes of this module are:
- develop familiarity with models of innovation and the marketing and technology interface;
- understand the importance of new product development to firm performance;
- learn methods of generating, evaluating, and testing product ideas;
- identify relevant components and plan a product launch;
- learn methods of evaluating and monitoring the success of a launch
Theoretical foundations and practical application of marketing of services examined. Topics include the nature of services, marketing framework and the marketing mix for services, service encounter, human factor, and service quality. This module focuses on the key elements (culture, communications, strategy, operations, people, and technology) that marketers must integrate to establish and sustain service excellence and provide customer value. While the module examines broad issues in managing service businesses and the service component of manufacturing firms, a core theme is how customer value is created. Topics include the nature of service products, consumer behavior in service settings, service quality and satisfaction, developing service strategies, managing customer service, service cape strategies, service recovery, and service technologies.
BBA in Entrepreneurship
Family-owned enterprises face particular challenges. The Family Enterprise Challenge is designed to help you address the universal issues as they apply to your own business and family. It combines rigorous learning with practical workshops.
This module leads you through different Marketing case studies of real companies using the Harvard Business School Case method
This module guides you through various Marketing case studies of real businesses using the Harvard Business School Case method.
The module’s primary objective is to develop a comprehensive understanding of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) from the corporate executive’s perspective. This module will cover all significant elements of the acquisition process, including corporate strategy, valuation, due diligence, financing decisions, transaction structures, restructuring options, takeover defense, and integration. It will also use cases and real-world applications to develop the skills necessary to prepare and evaluate the rationale for a proposed transaction.
BBA in Finance
This module aims to help students develop their skills in some important aspects of Corporate Finance. In particular, students will learn about the structure of the Financial Marketplace, how to evaluate Bonds and Common Stocks, and the techniques of capital structure and intermediate-term financing.
This module introduces students to the subject of strategy and helps them better understand the overall impact of internal and external influences on the firm. The essential purpose of the module is to provide the student with broad insights into the practice of strategic management and its real significance in contemporary multinational corporations.
This module aims to help students acquire skills in correctly using Cost Accounting to support corporate decisions. In particular, students will learn how to work with Cost Configurations, allocate Costs, develop Profitability Analysis, calculate process/ product costs, and the Activity-Based Costing methodology. Finally, students will learn some fundamentals of Planning / Budgeting together with principles of Variance Analysis.
Cost of the program
Sophomore year
| Application fee | € 200 – due immediately |
| Enrollment fee | € 3,050 – due immediately after acceptance |
| First Installment | € 2,400 – due after two months |
| Second Installment | € 2,400 – due after four months |
| Total Tuition Fees | € 8,050 |
Junior Year
| Administration fee | € 200 – due immediately |
| Enrollment fee | € 3,250 – due immediately after acceptance |
| First Installment | € 2,800 – due after two months |
| Second Installment | € 2,800 – due after four months |
| Total Tuition Fees | € 9,050 |
Senior Year
| Administration fee | € 200 – due immediately |
| Enrollment fee | € 4,000 – due immediately after acceptance |
| First Installment | € 3,000 – due after two months |
| Second Installment | € 3,000 – due after four months |
| Total Tuition Fees | € 10,200 |
IMPORTANT: The above tuition and fees do not include the access to our Digital Library, which has an additional cost of 100€ per academic year.
The above tuition fees are for the SSM in Residence Programs in Rome, Barcelona and Brescia. At Swiss School of Management we firmly believe in equity by giving people around the globe the same opportunities to earn an SSM degree. For students applying from areas of the planet with unequal social or economic conditions, we offer different rates. Please contact our in Residence Programs Directors in UAE, GCC, & Cairo as tuition fees vary.
Learn more about our Refund Policy.
